Industrial Piston Compressors: The Workhorses of Compressed Air Systems
In the world of industrial machinery, compressed air is often referred to as the “fourth utility,” following electricity, water, and gas. At the heart of many compressed air systems lies a tried-and-true technology that continues to power industries across the globe: the industrial piston compressor. Known for its durability, versatility, and affordability, the piston compressor—also called a reciprocating compressor—remains a popular choice for factories, workshops, and remote industrial sites alike.
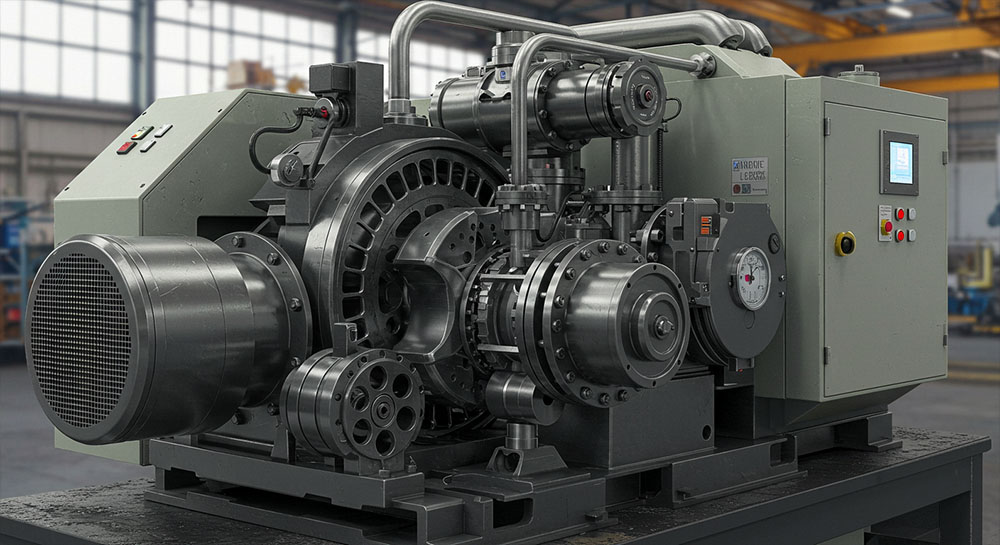
What Is an Industrial Piston Compressor?
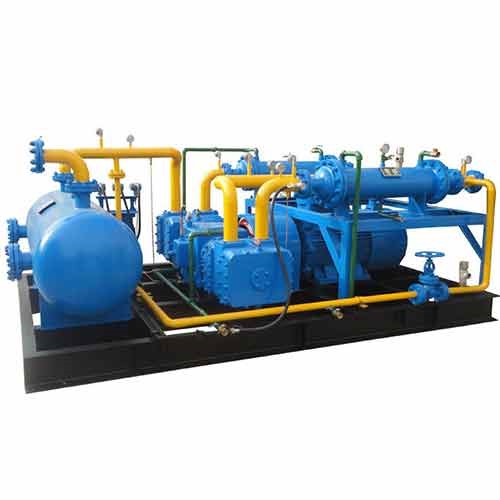
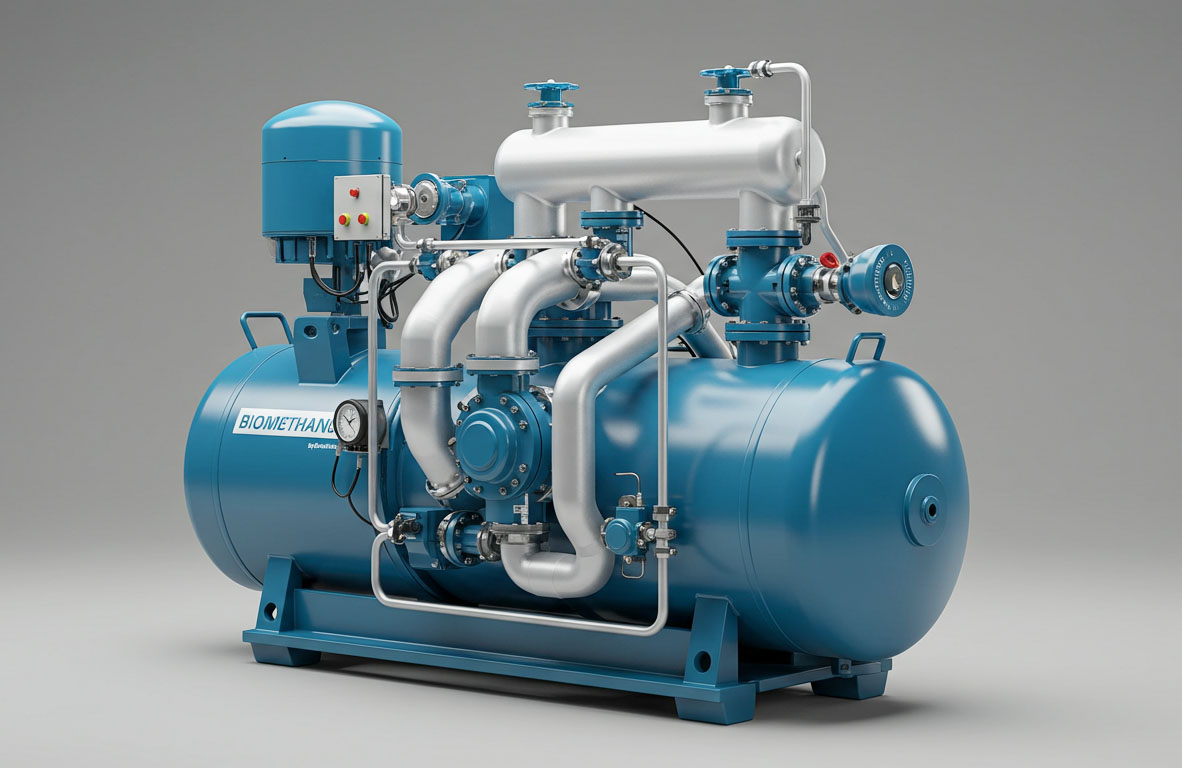
An industrial piston compressor is a type of positive displacement compressor that works by using one or more reciprocating pistons to compress and deliver air at high pressure. The process begins when a piston moves down inside a cylinder, creating a vacuum that draws in ambient air through an intake valve. As the piston moves up, it compresses the trapped air and pushes it through an outlet valve into a storage tank or directly into a pneumatic system.
Piston compressors can be powered by electric motors or internal combustion engines, and they come in a wide variety of configurations to suit different industrial applications.
Key Components and How They Work
An industrial piston compressor typically consists of the following components:
- Cylinders – The chambers where air compression takes place.
- Pistons – Move up and down inside the cylinders to compress air.
- Crankshaft and Connecting Rod – Convert rotational motion into the linear motion of the piston.
- Valves – Control the flow of air in and out of the cylinder.
- Cooling System – Usually air-cooled or water-cooled to manage the heat produced during compression.
- Lubrication System – Keeps moving parts functioning smoothly and reduces wear.
Single-stage piston compressors compress air in one stroke, while two-stage (or multistage) compressors compress air in successive stages, enabling higher pressures and improved efficiency.
Advantages of Piston Compressors in Industrial Use
1. Proven Technology
Piston compressors have been around for over a century and are backed by decades of engineering improvements. They are simple, robust, and well-understood machines, making them easy to maintain and repair.
2. High Pressure Capabilities
Industrial piston compressors can deliver air at pressures ranging from 100 PSI to well over 1000 PSI, depending on the design. This makes them ideal for high-pressure applications like PET bottle blowing, industrial gas handling, and pipeline testing.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to screw or centrifugal compressors, piston compressors are typically more affordable, especially for low to moderate duty cycles. Spare parts and service are widely available, further reducing long-term costs.
4. Versatility
They are suitable for a wide variety of gases—including air, nitrogen, hydrogen, helium, CO₂, and other specialized gases—and are widely used in industries such as:
- Manufacturing and assembly
- Oil and gas
- Chemical and pharmaceutical production
- Food and beverage processing
- Automotive repair and service
Common Industrial Applications
- Workshops and Fabrication Plants
Pneumatic tools such as grinders, sanders, and nail guns rely heavily on piston compressors. Their ability to start and stop quickly makes them ideal for intermittent-use applications. - Gas Handling
In chemical plants and refineries, piston compressors are used for compressing and transferring process gases, including flammable and corrosive types. - Medical and Laboratory
Oil-free piston compressors are used to supply clean, dry air for laboratories, hospitals, and dental clinics. - Bottling and Packaging
In PET bottling operations, high-pressure piston compressors provide the power needed to form plastic bottles from preforms. - Energy Sector
In natural gas compression and transmission, piston compressors play a key role in boosting pressure in pipelines and gas storage systems.
Maintenance and Reliability
While industrial piston compressors are tough machines, proper maintenance is crucial to ensure performance and longevity. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Regular oil changes for lubricated models
- Filter replacements to protect valves and cylinders
- Belt tension checks on belt-driven units
- Valve inspection and reseating or replacing worn components
- Leak detection in the piping system
Modern compressors may include built-in diagnostic tools or programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to monitor operating conditions and flag potential issues early.
Oil-Lubricated vs. Oil-Free Models
Choosing between oil-lubricated and oil-free piston compressors depends on the application:
- Oil-lubricated compressors are common in heavy-duty industrial use. They offer excellent cooling and reduced wear, making them suitable for long operational periods.
- Oil-free compressors are essential in environments where air purity is critical (e.g., food processing, pharmaceuticals, electronics). These compressors use special coatings or dry-running parts to eliminate the risk of oil contamination.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite their many benefits, piston compressors are not ideal for every situation. Their main limitations include:
- Noise and vibration – These machines are louder than rotary screw compressors and may require enclosures or isolation pads in sensitive environments.
- Duty cycle – Most piston compressors are not designed for continuous use. Overheating can occur if the machine runs for extended periods without rest.
- Size and weight – Larger, high-capacity piston compressors can be bulky and require strong foundations for stability.
For applications requiring continuous operation and quiet performance, rotary screw or scroll compressors may be a better fit.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Although piston compressors are based on old principles, modern innovations are enhancing their performance:
- Variable speed drives (VSDs) are now available on some models, improving efficiency by adjusting motor speed based on demand.
- Digital monitoring and IoT integration allow for real-time condition tracking, predictive maintenance, and better energy management.
- Advanced materials such as ceramic or carbon-coated pistons and cylinders reduce wear and allow for longer maintenance intervals.
Manufacturers are also optimizing airflow and reducing noise levels to make these machines more competitive with newer compressor types.
Conclusion
Industrial piston compressors continue to be a backbone of compressed air systems around the world. Their simplicity, rugged construction, and ability to handle diverse applications make them indispensable in countless industries. With proper maintenance and thoughtful application, a well-built piston compressor can serve reliably for years—even decades.


