Mastering the Power: A Comprehensive Guide to Gas-Powered Air Compressors
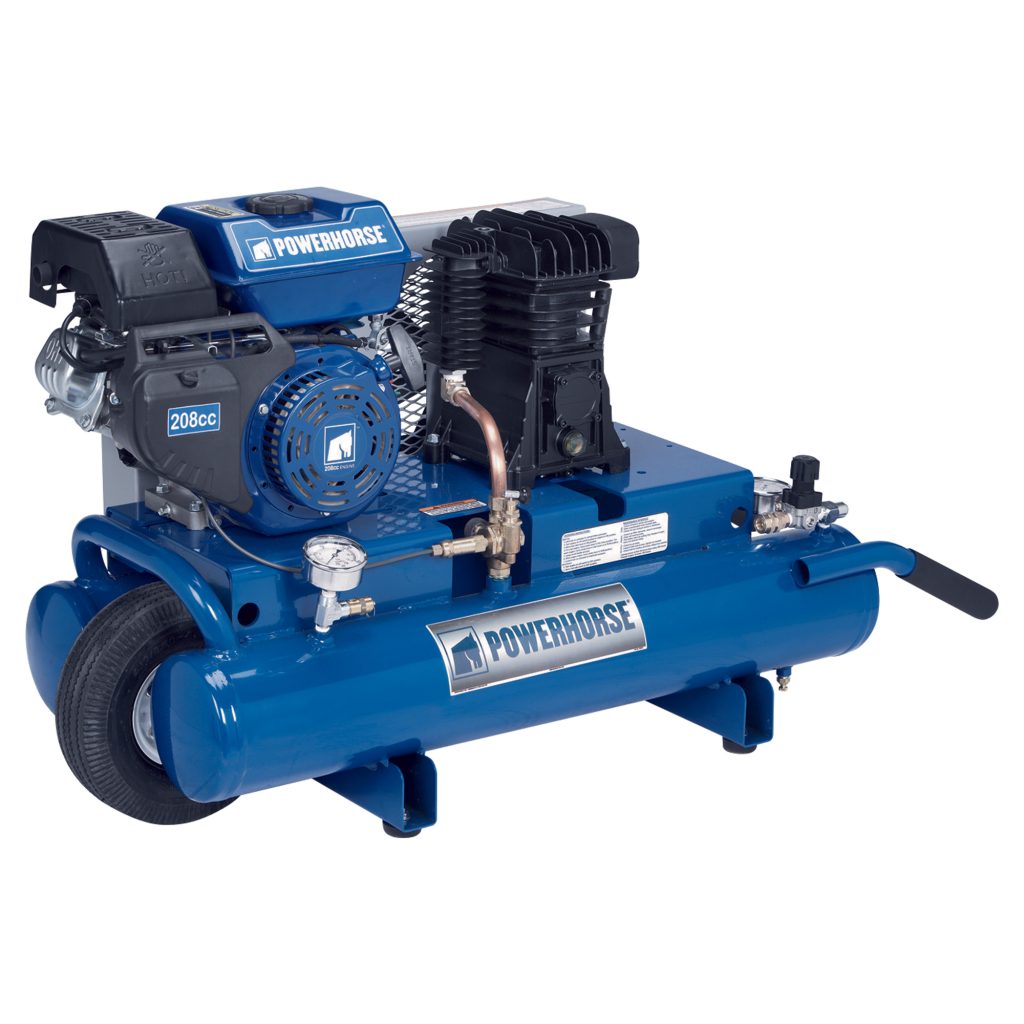
A gas-powered air compressor is a type of air compressor that is driven by a gasoline engine. Unlike electric air compressors, these are independent of electrical power sources, making them highly portable and suitable for use in remote locations or on job sites without power access. Here are some key features and considerations for gas-powered air compressors:

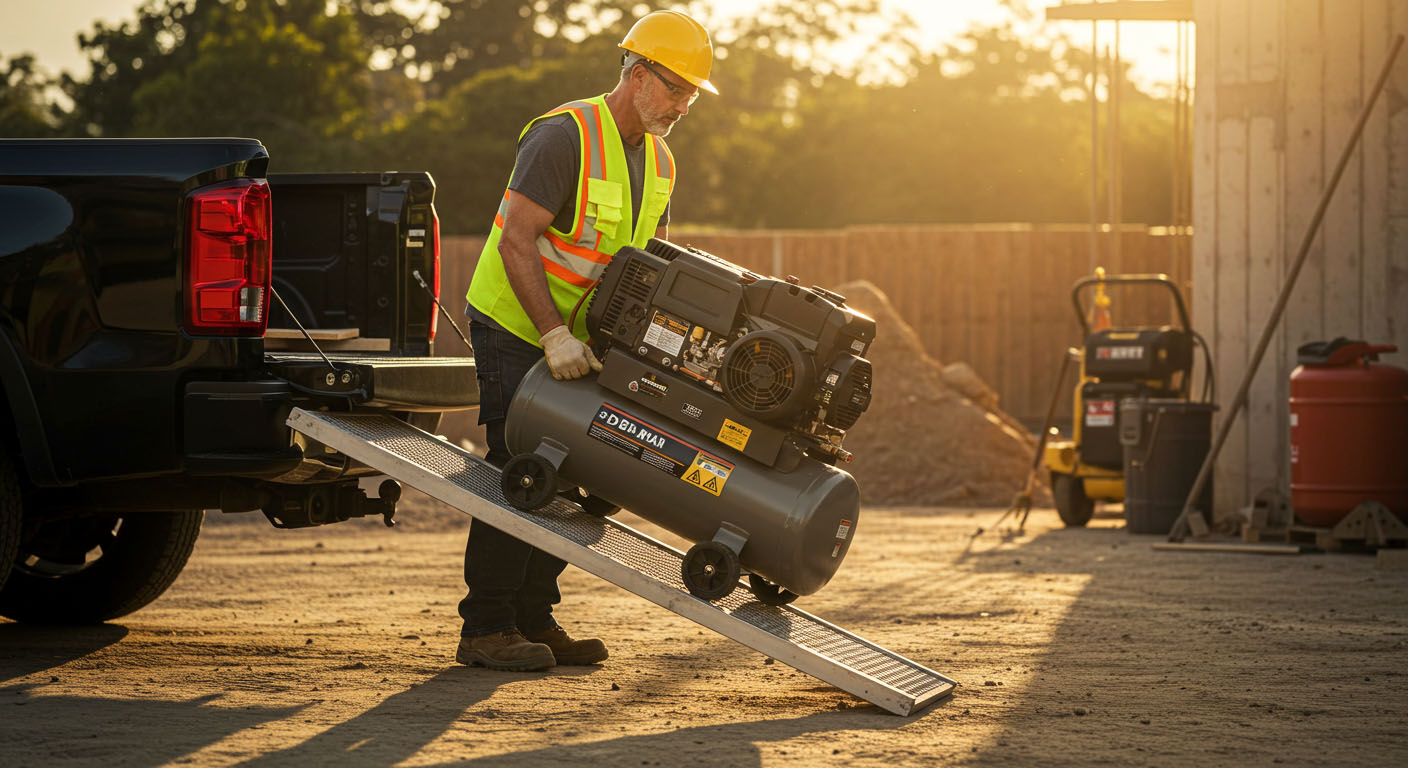
- Portability: Gas-powered air compressors are designed for mobility. They are ideal for construction sites, road work, and other outdoor applications where electricity might not be readily available.
- Power Source: They run on gasoline, which means they require proper ventilation for exhaust gases. This makes them unsuitable for indoor use without adequate ventilation.
- Capacity and Performance: These compressors come in various sizes and capacities, suitable for everything from light tasks like powering nail guns to heavy-duty applications like running jackhammers or sandblasting equipment.
- Noise Level: They tend to be louder than their electric counterparts, which is a consideration in noise-sensitive areas.
- Maintenance: Gas-powered compressors require regular maintenance, including engine checks, oil changes, and fuel monitoring, to ensure efficient and reliable operation.
- Cost of Operation: The operational costs can be higher due to the need for gasoline, which may fluctuate in price. However, the trade-off is greater mobility and independence from electrical power sources.
- Environmental Considerations: Since they emit exhaust gases, they are less environmentally friendly compared to electric compressors. This factor might be important in areas with strict environmental regulations.
- Durability: Generally, gas-powered air compressors are built to be robust and durable, as they are often used in demanding and harsh outdoor conditions.
Advantages of Gas-Powered Air Compressors
Gas-powered air compressors offer a range of advantages, chief among them being their portability, power, and versatility, making them an invaluable tool in various settings.
Portability: One of the most significant benefits of gas-powered air compressors is their portability. Unlike their electric counterparts, they are not tethered to a power source, allowing them to be used in remote or undeveloped sites where electricity is unavailable or unreliable. This mobility is particularly advantageous in construction, roadwork, and agricultural settings. The US address generator can streamline administrative tasks, enabling users to create necessary addresses on the fly, and saving time and effort in logistical operations.
Power and Efficiency: Gas-powered compressors are known for their robust power output, which makes them ideal for heavy-duty tasks that require high air pressure. They can operate larger tools and equipment efficiently, making them a preferred choice in construction and industrial applications. Their engines are designed to deliver consistent power, ensuring that tools operate at optimal performance levels, which is particularly crucial in high-demand situations.
Versatility: The versatility of gas-powered air compressors is evident in their widespread use across various industries. From powering pneumatic tools in construction sites to facilitating operations in agricultural farms and even in disaster relief efforts where electricity is non-existent, these compressors prove to be an indispensable tool. Their adaptability to different working conditions and their ability to handle a range of tasks make them a versatile addition to any workforce.
How To Choosing the Right Gas-Powered Air Compressor
Selecting the right gas-powered air compressor involves considering various factors, including capacity, size, key features, and the brand’s reputation for quality. These considerations ensure you choose a compressor that aligns with your specific needs and offers reliability and efficiency.
Capacity and Size: The capacity and size of a gas-powered air compressor are determined by the intended use. For light tasks like powering nail guns or inflating tires, a smaller, more portable unit may suffice. However, for more demanding jobs like operating heavy pneumatic tools or sandblasting, a larger compressor with a higher capacity is necessary. Consider the tools you plan to use and their air consumption (measured in CFM – cubic feet per minute) and match the compressor’s output to these requirements. Additionally, think about the space you have available for the compressor and whether portability is a key factor for your applications.
Features to Consider: Essential features to evaluate include tank size, PSI (pounds per square inch) ratings, and engine type. A larger tank will hold more air, allowing for longer tool operation times before the motor needs to restart. Higher PSI ratings mean the compressor can store more air in the tank, useful for tools requiring high pressure. The engine type should be reliable and powerful enough to meet your demands, with a good balance between fuel efficiency and performance.
Brand and Quality: Investing in a compressor from a reputable brand is crucial. Renowned brands generally offer better quality, reliability, and after-sales support, including access to spare parts and service centers. High-quality models might come at a higher upfront cost but often translate to better performance, longer lifespan, and lower maintenance costs in the long run.
Usage Scenarios and Applications
Gas-powered air compressors are versatile tools, widely used across various sectors like construction, agriculture, and industrial manufacturing, each with unique requirements.
Construction and Building: On construction sites, gas-powered air compressors are indispensable. Their portability allows them to be easily moved around large sites or in areas where electricity is not readily available. They power a variety of tools essential for building, such as pneumatic nail guns, staplers, and paint sprayers. Their robustness makes them suitable for more demanding tasks as well, like operating jackhammers or concrete compactors, which are crucial in foundational work and demolition.
Agriculture: In the agricultural sector, these compressors play a vital role in a range of tasks. They are used in powering equipment for crop spraying, dairy operations, and livestock management tools. Their mobility is especially beneficial in the vast expanses of farms and ranches where electrical power might not be easily accessible. Moreover, they assist in maintenance tasks like fence building or repair, where pneumatic tools can significantly speed up the work.
Industrial and Manufacturing: In industrial settings, gas-powered compressors are used for both routine tasks and specialized applications. They power pneumatic assembly tools, material handling equipment, and are also used in product finishing processes like sandblasting or spray painting. In manufacturing, they facilitate various processes, including operating automated machinery, providing control air for valves, and in packaging and sorting operations.
Gas Powered Air Compressor Maintenance and Upkeep
Proper maintenance and upkeep are essential for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of gas-powered air compressors. Regular checks and diligent engine care can significantly extend the life of your compressor and prevent costly repairs.
Regular Checks: Routine maintenance should include checking and cleaning air filters, as clogged filters can reduce efficiency and strain the engine. Regularly inspect hoses and connections for leaks or wear and ensure that the air intake is clear of debris. Also, monitor the compressor’s oil level and quality, as well as the condition of belts and other moving parts. Keeping a log of these checks can help track the compressor’s condition over time and preemptively address issues.
Engine Care: The engine is the heart of your gas-powered air compressor, and proper care is crucial. Regular oil changes, as recommended by the manufacturer, are vital for engine health. Use the correct type and grade of oil and check the oil level before each use. Fuel management is also important; use clean, fresh gasoline and avoid leaving fuel in the engine for prolonged periods of inactivity, as this can lead to fuel system issues. Regularly inspect the spark plug and replace it if necessary.
Troubleshooting Common Issues: Familiarize yourself with common problems like difficulty starting, unusual noises, or loss of pressure. A hard-starting engine might indicate issues with fuel quality or a dirty spark plug. Unusual noises can be a sign of internal wear or loose components. Loss of pressure might suggest leaks or a malfunctioning pressure switch. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more significant problems and ensure consistent performance.
Safety and Operational Best Practices
Safety and efficient operation are paramount when using gas-powered air compressors. Adhering to best practices ensures not only the longevity of the equipment but also the safety of the users and the environment.
Safety Measures: Due to the combustible nature of gasoline, proper handling and storage are essential. Always refuel in a well-ventilated area, away from any ignition sources, and store fuel in approved containers. The high noise levels of gas compressors necessitate the use of hearing protection to prevent hearing damage during extended use. Additionally, since these compressors emit exhaust fumes, they should never be used indoors or in poorly ventilated spaces to avoid carbon monoxide poisoning.
Efficient Operation: To maximize efficiency and conserve fuel, properly warm up the engine before heavy use and avoid running the compressor more than necessary. Regular maintenance, as per the manufacturer’s guidelines, keeps the compressor running efficiently. Using the correct type and amount of oil and keeping air filters clean also contribute to fuel efficiency.
Environmental Considerations: Gas-powered air compressors emit exhaust gases, contributing to air pollution. When possible, opt for models with lower emissions or use them in conjunction with emission-reduction strategies. Be mindful of noise pollution as well, especially in residential or noise-sensitive areas. Using silencers or noise barriers and operating the compressor only during appropriate hours can help mitigate noise impact.
Comparing Gas-Powered and Electric Compressors
When choosing between gas-powered and electric air compressors, understanding their respective pros and cons, as well as their suitability for different applications, is crucial.
Gas-Powered Compressors: The primary advantage of gas-powered compressors is their portability and independence from electrical power sources, making them ideal for outdoor, remote, or mobile applications. They generally offer greater power output, which is beneficial for heavy-duty tasks. However, they are louder, emit exhaust fumes, and require more maintenance, including regular fuel and oil changes. Their use in enclosed or poorly ventilated spaces is also a safety concern due to carbon monoxide emissions.
Electric Compressors: Electric models are quieter, more environmentally friendly, and typically easier to maintain, as they don’t require fuel changes or engine servicing. They are better suited for indoor use or in areas with strict noise and emission regulations. However, their dependency on an electrical source limits their mobility and makes them less suitable for sites without power access. They also tend to have less power output compared to gas-powered models, which may be a consideration for heavy-duty applications.
Application Suitability: The choice depends largely on the intended use. For indoor applications, or where noise and emissions are a concern, electric compressors are preferable. Conversely, for outdoor, high-powered applications, or in areas without reliable electricity, gas-powered compressors are the better option. Understanding the specific requirements of your tasks, including power needs, mobility, and environmental considerations, will guide you in making the most suitable choice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gas-powered air compressors offer unmatched portability and power, making them ideal for a variety of outdoor and heavy-duty applications. However, their maintenance, safety considerations, and environmental impact require careful attention. Choosing the right compressor, coupled with proper maintenance and operation, ensures optimal performance and longevity of your equipment.